A sophisticated multi-stage phishing campaign has been meticulously observed targeting users across Russia, deploying a potent combination of ransomware and the insidious Amnesia Remote Access Trojan (RAT). This elaborate operation highlights a growing trend in cyber warfare, where attackers employ complex methodologies to bypass defenses and achieve deep system compromise.
The Deceptive Opening: Social Engineering at its Core
According to Cara Lin, a researcher at Fortinet FortiGuard Labs, the attack’s genesis lies in highly convincing social engineering tactics. “The attack begins with social engineering lures delivered via business-themed documents crafted to appear routine and benign,” Lin detailed in a recent technical breakdown. These seemingly innocuous documents, coupled with accompanying scripts, serve as a clever visual distraction. While victims are engrossed in what appears to be a legitimate task or status update, the malicious activity quietly unfolds in the background, out of sight and often, out of mind.
Multi-Cloud Resilience and Stealthy Distribution
A hallmark of this campaign is its strategic utilization of multiple public cloud services, enhancing both its resilience and stealth. GitHub is primarily leveraged for distributing initial scripts, while the more potent binary payloads are discreetly staged on Dropbox. This deliberate separation of infrastructure significantly complicates takedown efforts, granting the campaign a remarkable degree of operational longevity.
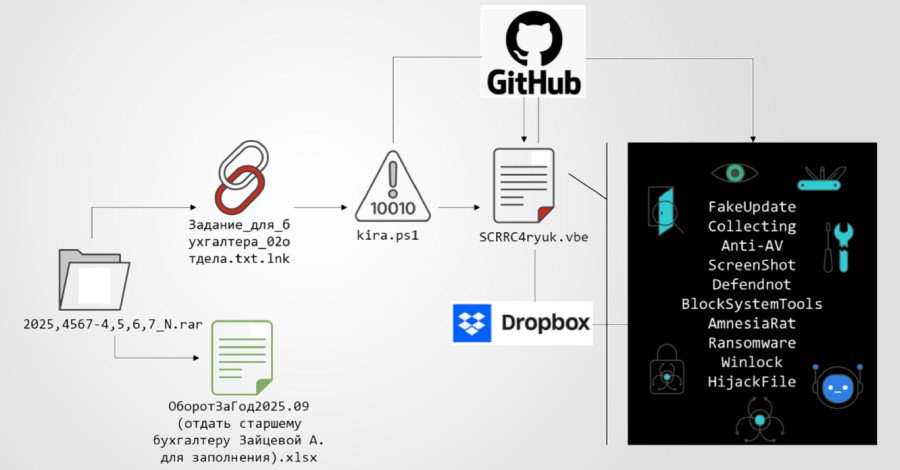
The initial infection chain is initiated through compressed archives, distributed via social engineering. These archives contain multiple decoy documents alongside a malicious Windows shortcut (LNK) file, cunningly disguised with Russian-language filenames. A double extension, such as “Задание_для_бухгалтера_02отдела.txt.lnk”, further reinforces the illusion of a harmless text file.
Upon execution, this LNK file triggers a PowerShell command. This command retrieves a subsequent PowerShell script from a GitHub repository, acting as a crucial first-stage loader. Its immediate tasks include establishing a foothold, preparing the system to conceal malicious traces, and seamlessly handing off control to later stages of the attack.
Evasive Maneuvers: Disarming Defenses and Gathering Intelligence
The attackers demonstrate a profound understanding of system defenses, employing a series of advanced techniques to suppress visibility and neutralize endpoint protection.
Stealth Execution and Decoy Deployment
Fortinet researchers noted that the PowerShell script first “suppresses visible execution by programmatically hiding the PowerShell console window,” eliminating immediate visual cues of its operation. Simultaneously, it generates and automatically opens a decoy text document in the user’s local application data directory. This keeps the victim engaged and oblivious while the true malicious processes run silently.
Crucially, once the decoy is displayed, the script communicates with the attacker via the Telegram Bot API, confirming the successful execution of the first stage. A calculated 444-second delay precedes the execution of a highly obfuscated Visual Basic Script (“SCRRC4ryuk.vbe”), also hosted on GitHub. This VBScript serves as a dynamic controller, assembling subsequent payloads directly in memory, thus avoiding disk artifacts and allowing threat actors to update or swap payload functionality without altering the core attack chain.
Bypassing Microsoft Defender with ‘Defendnot’
A particularly audacious characteristic of this campaign is the operational abuse of ‘defendnot’. This tool, released last year by security researcher es3n1n, tricks Microsoft Defender into believing another antivirus product is already installed on the Windows host, prompting Defender to disable itself to prevent conflicts. The malware further solidifies its control by:
- Configuring Microsoft Defender exclusions for critical directories (ProgramData, Program Files, Desktop, Downloads, system temporary directory).
- Using PowerShell to disable additional Defender protection components.
- Tampering with Registry-based policy controls to disable Windows administrative and diagnostic tools.
- Implementing a file association hijacking mechanism, redirecting attempts to open certain file types to a message instructing victims to contact the attackers via Telegram.
Persistent Reconnaissance and Data Exfiltration
Beyond disabling defenses, the campaign actively conducts reconnaissance. A dedicated .NET module, downloaded from GitHub, captures screenshots every 30 seconds, saving them as PNG images and exfiltrating this visual intelligence using a Telegram bot. This constant surveillance provides attackers with a real-time view of the compromised environment.
The Final Blow: Amnesia RAT and Ransomware Deployment
After systematically disarming security controls and recovery mechanisms, the campaign unleashes its primary payloads. One of the most significant is the Amnesia RAT (“svchost.scr”), retrieved from Dropbox. This potent remote access trojan is designed for extensive data theft and remote control capabilities. Amnesia RAT is adept at pilfering sensitive information from web browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, Discord, Steam, and Telegram. It also collects system metadata, captures screenshots, webcam images, microphone audio, clipboard contents, and active window titles. Its full remote interaction capabilities include process enumeration and termination, along with shell command execution, granting attackers unparalleled control over the compromised system. While the article mentions ransomware, the specifics of the ransomware itself are not detailed, implying it’s deployed as another final-stage payload after the RAT establishes a strong foothold.
This multi-faceted attack underscores the evolving sophistication of cyber threats. Organizations and individuals, particularly in targeted regions, must remain vigilant and bolster their defenses against such elaborate and persistent campaigns.
For more details, visit our website.
Source: Link








Leave a comment